CNC turning or milling? Discover which process is best for your needs. Learn the key differences, advantages, and ideal applications.
CNC turning and CNC milling. They sound like two sides of the same coin, right? Well, they are similar, but with distinct differences that make a big impact on your final product. Choosing the wrong one can mean wasted time and money – and nobody wants that.

What is CNC Milling & CNC Turning?
CNC Milling Process Description
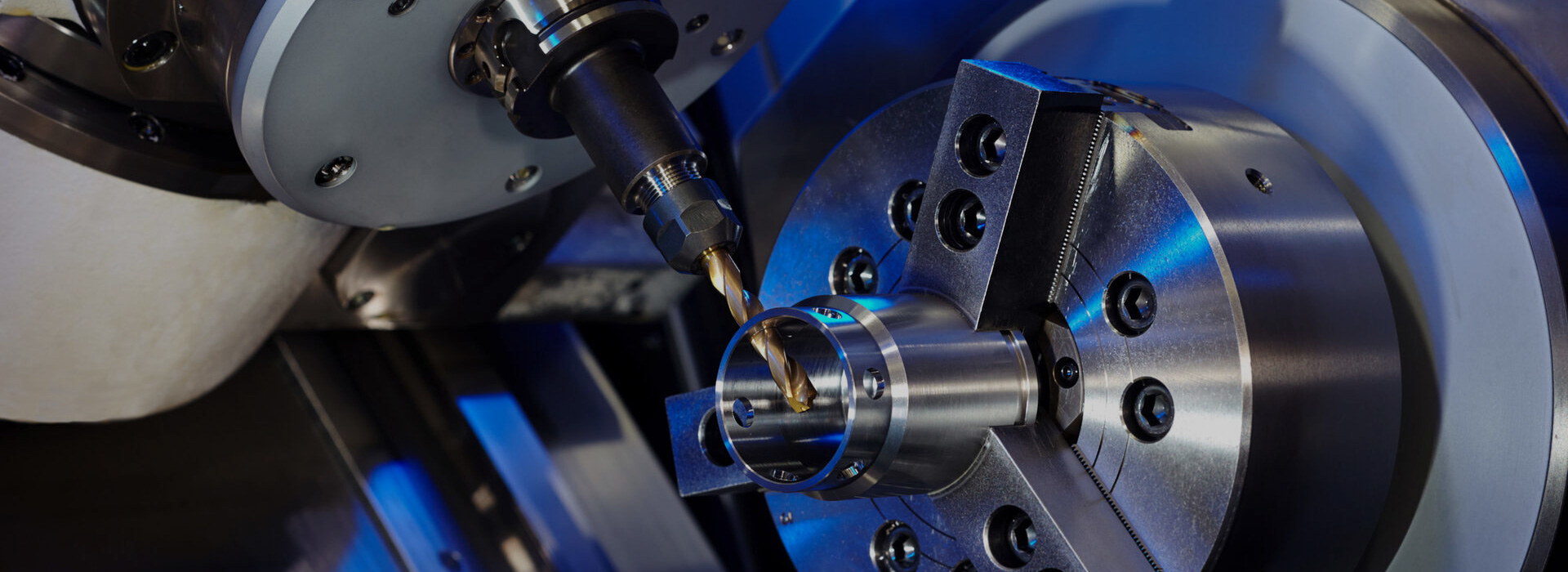
CNC milling involves the use of rotating tools to rapidly remove material from a workpiece to form complex shapes. The milling cutter moves forward at a certain angle to remove the surface of the material. The object to be processed by the CNC milling machine is fixed at a certain position on the machine tool, and the milling cutter rotates at high speed under the clamping of the fixture. The process is guided by computer-controlled motion along multiple axes, ensuring unmatched accuracy and repeatability.
CNC Turning Process Description
In CNC turning, the workpiece rotates relative to a fixed cutting tool, enabling computer-guided external material removal. The machining principle is that the workpiece rotates and the tool is fixed. On this machine, the material can rotate but the tool remains stationary. The cylindrical symmetry involved lends itself to turning to precisely manufacture shafts, pins, and other rotationally symmetrical parts.
CNC Turning vs. CNC Milling: Pros and Cons
Both CNC turning and milling have their own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these will help you pick the perfect process for your project.
Pros and Cons of CNC Milling
Pros
● It can create parts of varying complexity, from simple geometries to intricate designs.
● CNC milling operations can achieve a high degree of accuracy, producing parts with tight tolerances and complex features.
● Milling is suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
● CNC milling generally produces a better surface finish than CNC turning, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics or surface quality are critical.
Cons
● CNC milling machines are more expensive than CNC lathes. This is because they have additional axes of motion and are more complex.
● Milling operations generally require longer setup times than turning because the cutting tool must be precisely aligned and programmed for each specific part geometry.

Pros and Cons of CNC Turning
Pros
● It is an effective choice for parts with rotational symmetry.
● CNC turning lathes generally have shorter setup times than CNC milling machines because the cutting tool only needs to be aligned along two axes.
● Generally speaking, CNC turning is cheaper than milling, making it a more cost-effective choice.
Cons
● CNC turning is limited to cylindrical shapes and features, so it is not very suitable for complex geometries.
● Although it can achieve a high-quality surface finish, it is generally not as good as the surface finish produced by CNC milling.

What is the Difference between CNC milling and CNC turning?
1) Motion Trajectory
CNC turning: The workpiece rotates and the turning tool moves along a straight line or curve.
CNC milling: The milling cutter rotates and the workpiece moves along a straight line or curve.
2) Mechanical Configuration
CNC turning: Using CNC lathes or lathes, processing including drilling, reaming, tapping and knurling can also be performed.
CNC milling: Using CNC milling machines or milling machines, planes (horizontal, vertical), grooves (keyways, T-slots, dovetail grooves), gears, helical surfaces (threads, spiral grooves) and various curved surfaces can be processed.
3) Workpiece Shape
CNC turning: Mainly used for processing internal and external cylindrical or conical surfaces, such as shafts, bushings, sleeves, etc.
CNC milling: Specially formed surfaces used for machining flat and irregular surfaces such as grooves, grooves, gears, threads and dies to create complex shapes and features
4) Tool function
CNC turning: Single-point tool
CNC milling: Multi-point tool
5) Cutting method
CNC turning: Continuous cutting, keeping the cutting tool in contact with the workpiece
CNC milling: Intermittent cutting, tool teeth engagement and disengagement
6) Chips
CNC turning: Chips, discontinuous or continuous chips
CNC milling: Always produces discontinuous chips
How To Choose The Right CNC Process For Your Project
Now that you know the strengths and weaknesses of each process. Choosing between CNC turning and milling largely depends on the types of parts you need to produce. Here's a quick guide to help you make the right call:
When to Choose CNC Turning?
●Round and Round: If your part is primarily cylindrical, turning is usually the way to go. Think shafts, pins, bolts, and anything else with a central axis.
●Need for Speed: If you need to produce a large number of simple, symmetrical parts quickly, turning will likely be faster and more efficient.
●Smooth Finish is Key: When a smooth surface finish is critical, turning often provides better results than milling.
Examples: Think of everyday objects like doorknobs, screws, and even baseball bats. These are all great examples of parts that are typically made using CNC turning.
When to Choose CNC Milling?
●Complex Geometries: If your part has intricate details, and sharp corners, or requires milling from multiple sides, then CNC milling is the clear winner.
●Variety is the Spice of Life: When you need to create parts with a wide range of shapes and features, milling offers the flexibility to get the job done.
●One-offs and Prototypes: For small production runs or prototypes, milling can be more cost-effective than turning, as it doesn't require specialized tooling.
Examples: Engine blocks, gears, and complex molds are all examples of parts that are often produced using CNC milling.
Applications of CNC Milling and Turning
| Industry | CNC Milling Applications | CNC Turning Applications |
| Aerospace | - Structural components (fuselage panels, ribs, spars) - Engine components (turbine blades, casings) | - Turbine shafts, engine parts, landing gear components - Precision parts for aircraft systems |
| Automotive | - Engine parts (pistons, cylinder heads, blocks) - Transmission parts (gear housings, shafts) | - Shafts, brake components, camshafts, crankshafts - Drive shafts, steering components |
| Medical | - Surgical instruments (forceps, scalpels, implants) - Medical devices (pacemakers, prosthetics, joints) | - Orthopedic implants, dental tools, surgical components - Medical shafts, rods, precision components |
| Oil & Gas | - Custom components (valves, housings) - Tooling for drilling equipment | - Valve stems, seats, flanges, pipe fittings - Drill shafts, fluid control systems |
| Electronics | - Enclosures, housings for devices (computers, phones,keyboards) - Heat sinks, brackets for cooling | - Rotary components (connectors, switches, motors) - Precision components (capacitors, knobs, dials) |
In Conclusion
When choosing between CNC milling and CNC turning, it is important to consider factors such as part geometry, material, accuracy requirements, surface finish, and production volume. Ultimately, the CNC machining process that is best for your project will depend on the specific requirements and constraints of your project.
If you are looking for a reliable and experienced partner to meet your CNC milling and CNC turning needs, BergekCNC offers CNC milling services, CNC turning services, and all other machining services with over 100 material options. Our team of experts is ready to help you achieve your manufacturing goals and provide high-quality, precision CNC turned parts. Please feel free to contact us and get a quote by simply submitting your design
Bergek CNC - CNC Machining Service Provider From China
Provides comprehensive CNC machining services based on customer applications
Get In Touch With Us!
Copyright © 2022 SHENZHEN BERGEK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. - www.bergekcnc.com All Rights Reserved.